Six Sigma is a powerful methodology that can significantly improve project management by reducing defects, waste, and variations in processes. When applied effectively, Six Sigma provides a structured approach to identify and eliminate the root causes of problems, leading to increased efficiency, productivity, and customer satisfaction.
This blog post will explore the key benefits of applying this methodology to project management and offer guidance on how to effectively integrate Six Sigma methodologies into your project management practices.
Understanding Six Sigma:
Definition:
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology that aims to improve processes by reducing defects and variations. It focuses on enhancing quality, increasing efficiency, and ultimately delivering better results for customers.
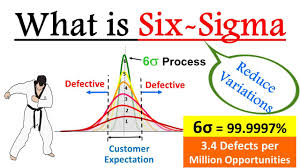
The goal of Six Sigma is to achieve a level of quality that is nearly perfect, with only 3.4 defects per million opportunities. This is achieved by using a structured approach called DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) to identify and eliminate causes of variation and improve processes.
Key Principles of Six Sigma:
The six key principles that guide the Six Sigma methodology are:
- Focus on the customer: Six Sigma always focuses on the customer, striving to improve constantly and meet their expectations. Deviations from a target represent instances where an outcome falls outside a customer’s expectation.
- Continuous improvement: Companies that embrace Six Sigma look constantly for new improvement opportunities. As soon as one process reaches the Six Sigma level of accuracy, the focus shifts to the next performance improvement plan.
- Process standardization: Six Sigma focuses on standardizing processes to reduce deviations from a target, which can result from varied methods used by different team members or divisions.
- Data-driven approach: Six Sigma relies on data and analysis to drive decision-making and identify root causes of problems, leading to more effective problem-solving.
- Involvement of stakeholders: Six Sigma requires a structured process where all stakeholders collaborate and contribute to finding solutions to complex problems.
- Flexibility and adaptability: Six Sigma projects need to be able to adapt to changes in processes, with employees motivated to accept and implement improvements.
These key principles guide organizations in implementing Six Sigma effectively to achieve operational excellence and deliver superior results for their customers.
Benefits of Six Sigma Project Management:
- Improved Quality
- Increased Efficiency
- Customer Satisfaction
- Data-Driven Decision-Making
Key Elements of Six Sigma Project Management:
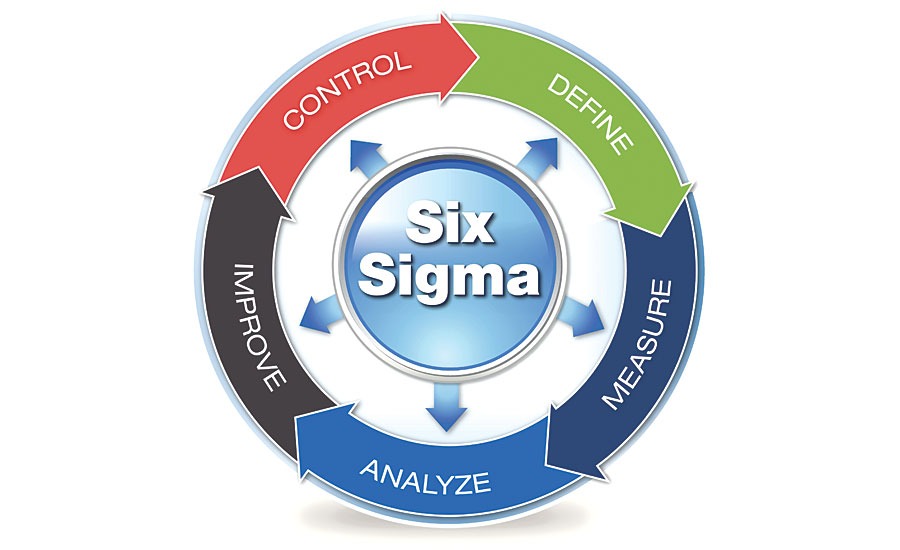
DMAIC framework (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control):
Here is the DMAIC framework presented in a table format:
| Phase | Description |
| Define | – Clearly define the problem, improvement opportunity, and project goals – Understand customer (internal and external) requirements – Create a project charter – Conduct voice of the customer analysis – Map the value stream |
| Measure | – Understand the current process performance – Collect relevant data and establish baseline metrics – Use process mapping, Pareto charts, and statistical analysis |
| Analyze | – Determine the root causes of variation or poor performance – Employ tools like root cause analysis, FMEA, and multi-vari charts – Uncover the underlying issues |
| Improve | – Develop and implement solutions to address the root causes – Use design of experiments, Kaizen events, and other improvement methods – Enhance process performance |
| Control | – Maintain the improvements made in the Improve phase – Develop a control plan and implement statistical process control (SPC) – Use mistake-proofing techniques to sustain the gains |
The DMAIC framework provides a structured, data-driven approach to problem-solving and continuous improvement, which is central to the Six Sigma methodology.
Statistical tools and techniques used in Six Sigma:
Here is a more concise summary of the key statistical tools and techniques used in Six Sigma:
1. Descriptive Statistics:
– Measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode)
– Measures of variability (standard deviation, range)
2. Process Capability Analysis:
– Metrics like Cp, Cpk, Pp, and Ppk
– Evaluates process stability and variation
3. Control Charts:
– X-bar, R, p, and c-charts
– Monitor process changes and identify variation sources
4. Histograms:
– Visualize data distribution and detect outliers
5. Pareto Charts:
– Identify and prioritize the most significant factors or defects
6. Cause-and-Effect Diagrams:
– Systematically categorize potential root causes
7. Scatter Plots:
– Analyze relationships between variables
8. Design of Experiments (DOE):
– Understand the impact of multiple variables on a process
9. Regression Analysis:
– Model and evaluate the influence of factors on outcomes
10. Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA):
– Evaluate and rank potential failure modes for risk assessment
These statistical tools and techniques enable Six Sigma practitioners to collect and analyze data, identify root causes, and implement effective solutions to improve processes and achieve desired quality and efficiency goals.
Aligning Six Sigma with project management constraints (scope, time, cost, quality):
Here is a simplified chart illustrating the alignment of Six Sigma with key project management constraints:
| Project Management Constraint | Alignment with Six Sigma |
| Scope | – Well-defined scope based on DMAIC framework – Alignment with organizational objectives and customer requirements |
| Time | – Structured timeline with defined milestones – Integration of project management techniques for timely completion – Effective communication and stakeholder management |
| Cost | – Focus on reducing costs through waste elimination and efficiency improvement – Data-driven approach to justify investment and demonstrate financial benefits – Use of project management tools for cost management |
| Quality | – Primary focus on achieving near-perfect performance – DMAIC framework and statistical tools for process quality improvement – Integration of project management practices for quality planning and control |
This chart highlights how Six Sigma can be effectively aligned with key project management constraints to drive successful project outcomes and deliver sustainable business results.
USE OUR TOOL NOW!
Elevate your projects with L6 Elite today! Discover enhanced efficiency and measurable advancements.
Implementing Six Sigma Project Management:
Implementing Six Sigma project management involves a structured approach to improving processes by reducing defects and variations. Here is a detailed guide on how to effectively implement Six Sigma:
1. Leadership Support
- Gain strategic management support to ensure commitment to the Six Sigma initiative.
- Communicate the need for improvement and secure active involvement from top management.
2. Training and Certification
- Provide necessary training to employees in Six Sigma methodologies.
- Certify designated employees as Yellow Belts, Green Belts, or Black Belts based on their level of expertise.
3. Establish Ownership
- Identify a Lean Six Sigma Champion or team responsible for leading the implementation.
- Ensure accountability and engagement throughout the organization.
4. Define What Value Is
- Determine what creates value for customers and align improvement efforts accordingly.
- Match customer expectations with organizational processes to identify areas for enhancement.
5. Set Priorities
- Prioritize improvement activities in line with strategic goals and customer requirements.
- Develop an action plan that supports the organization’s objectives and customer needs.
6. Gather Measurement Data
- Collect relevant data about the problem or process inefficiencies.
- Utilize problem-solving techniques like Value Stream Mapping and Pareto Chart analysis to identify root causes and prioritize improvement efforts.
7. Establish Control to Sustain Improvement
- Develop a control plan to monitor and sustain the achieved improvements.
- Create an environment that fosters continuous improvement, knowledge sharing, and collaboration across teams and departments.
USE OUR TOOL NOW!
Transform your projects with L6 Elite today! Discover a new level of streamlined efficiency and tangible improvements. Start your journey towards optimized success now!
By following these seven key steps, organizations can successfully implement Lean Six Sigma methodologies to reduce process inefficiencies, achieve greater business performance, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. This holistic approach combines Lean thinking with Six Sigma problem-solving techniques to identify root causes, measure operational efforts, and introduce a new organizational culture focused on delivering value to customers.
Critical Success Factors:
Based on the search results provided, here are the key critical success factors for implementing this method for project management in detail:
Leadership Support:
- Gain strategic commitment and active involvement from top management.
- Ensure visible, consistent support and an active role in communication and reward.
- Assure linkage of Six Sigma initiatives to corporate strategies and priorities.
- Require the use of facts and data to support decision-making at all levels.
- Create clear accountabilities, expectations, roles, and responsibilities.
- Conduct regular reviews to verify progress and provide oversight.
Training and Certification:
- Provide necessary training to employees on these methodologies.
- Certify designated employees as Yellow Belts, Green Belts, or Black Belts.
- Develop a Human Resources plan to support Six Sigma roles and responsibilities.
Effective Communication:
- Regularly communicate Six Sigma news, successes, and progress.
- Develop and disseminate communication aids to management.
- Advocate for and create a “common language” based on Six Sigma.
- Communicate pertinent Six Sigma information in every company meeting.
Project Management:
- Establish a documented 1-year project inventory and refresh it regularly.
- Ensure Six Sigma projects are aligned with critical business and customer needs.
- Assign a Champion and Black Belt to each project and hold them accountable.
- Implement a project tracking system to facilitate replication and reuse of successful projects.
Organizational Alignment and Buy-in:
- Link Six Sigma initiatives to the organization’s goals and objectives.
- Gain buy-in and support from top management, middle management, and employees.
- Emphasize the benefits of Six Sigma, such as better processes, happier customers, and a more supportive culture.
- Address fears and resistance to change through effective change management.
Continuous Improvement Culture:
- Foster a culture of continuous improvement and learning.
- Encourage knowledge sharing and collaboration across teams and departments.
- Establish control plans to monitor and sustain the achieved improvements.
By focusing on these critical success factors, organizations can effectively implement Six Sigma project management and achieve the desired operational excellence, quality improvements, and customer satisfaction.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, it’s important to gain buy-in and support from all levels of the organization for Six Sigma project management. Emphasize the benefits of Six Sigma and address any fears or resistance to change through effective change management. Foster a culture of continuous improvement and learning, and encourage knowledge sharing and collaboration across teams and departments. By focusing on these critical success factors, organizations can effectively implement this method and achieve operational excellence, quality improvements, and customer satisfaction.
FAQs:
Six Sigma project management is a methodology used to improve processes and eliminate defects in products and services. It focuses on data-driven decision-making and uses a set of tools and techniques to identify and remove the causes of defects and errors.
Implementing Six Sigma can lead to increased efficiency, cost savings, improved quality, and higher customer satisfaction. It can also help organizations to better understand their processes and make data-driven decisions for continuous improvement.
Critical success factors include gaining buy-in and support from all levels of the organization, establishing control plans to monitor and sustain improvements, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement and learning.
To address resistance to change, organizations can emphasize the benefits of Six Sigma, provide effective change management, and encourage knowledge sharing and collaboration across teams and departments.
Organizations can sustain improvements by implementing control plans to monitor processes, fostering a culture of continuous improvement, and encouraging collaboration and knowledge sharing across the organization.